Trade Act of 1974 – Treason against the American people
An Act to promote the development of an open, nondiscriminatory, and fair world economic system, to stimulate fair and free competition between the United States and foreign nations, to foster and economic growth of, and full employment in, the United States, and for other purposes.
H.R. 10710 – Introduced 10/3/1973, Public Law 93-618, 1/3/1975
China-Taiwan: One Country, Two Systems
One China policy. Taiwan is a special economic zone administratively separate from the mainland but politically, they are province of China.
H.R. 2479 – Taiwan Relations Act, Public Law 96-6, 4/10/1979
Macau, same arrangement as Taiwan. Macau – Special administrative/economic zone
One Country, Two Systems – Hong Kong, 1984 Concept of one country, two systems formalized.
Special Administrative Zones: Ports for Commerce
The Special Administrative Zones are ports subject to international maritime law and when the WTO was established in 1995, they are subject to international law under the WTO. The ports can be seaports or inland ports.
One America, Two Systems
The One America, two systems occurred in five phases. (1) The La Paz Treaty with Mexico which created a special economic zone over the U.S.-Mexican border – 1983. (2) The Free Trade Agreement with Canada signed in 1987. (3) Enterprise of the Americas Initiative, 1990 kicked off negotiations for the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) agreement which began the economic merger of the U.S., Canada and Mexico – law – 1993. World Trade Organization (end of Uruguay Round) 1994 (1995 effective) (4) Negotiations for the Free Trade Area of the Americas began at a summit in Miami in 1994, continued with annual summits became effective December, 2005. In 2005, the Security and Prosperity Partnership (SPP) was initiated to further solidify relations and continue the integration of the Americas.
Treason Timeline
In May of 1977, Presidents Carter and Lopez Portillo established the precursor to the BNC to provide better coordination of U.S. – Mexico relations. Then called the U.S. Mexico Consultative Mechanism it had three broad working groups–political, social and economics–and subgroups within each of these. At the first meeting in May 1978, Secretary of State Vance and Mexican Secretary of Foreign Relations Roel met in Mexico with the chairmen of the working groups to review the first year’s progress.
1981 – U.S. Mexico Binational Commission
“The Binational Commission was established in 1981 by Presidents Reagan and Lopez Portillo to serve as a forum for meetings between cabinet-level officials from both countries. The new BNC was envisioned as a simple, flexible tool that would meet once or twice annually with U.S. and Mexican counterparts addressing agendas of topics requiring high-level attention.”
1983 Special Economic Zone on the Border of Mexico and the U.S.
1983 – U.S.-Mexico treaty signed at La Paz, Mexico by Presidents Ronald Reagan and Miguel de la Madrid Hurtado establishing the international zone on the border. They wrapped the treaty in environmentalism but in fact, the international zone on the border was a special economic zone/administrative zone on the border between Mexico and the U.S. The border zone is a port zone because it is bounded by water on both sides.
Aug 14, 1983 – Remarks on Arrival in La Paz, Mexico, for Meetings With President Miguel de la Madrid Hurtado
Aug 14, 1983 – Toast at a Luncheon Hosted by President Miguel de la Madrid Hurtado of Mexico in La Paz
Aug 14, 1983 – Remarks Following Meetings With President Miguel de la Madrid Hurtado of Mexico in La Paz
Aug 14, 1983 – Joint Communique Following Discussions With President Miguel de la Madrid Hurtado of Mexico
Border Treaty with Mexico (La Paz Treaty)
Aug 14, 1983 – United States-Mexico Agreement on the Environment in the Border Area
Article 4
For the purposes of this Agreement, it shall be understood that the “border area” refers to the area situated 100 kilometers on either side of the inland and maritime boundaries between the Parties.
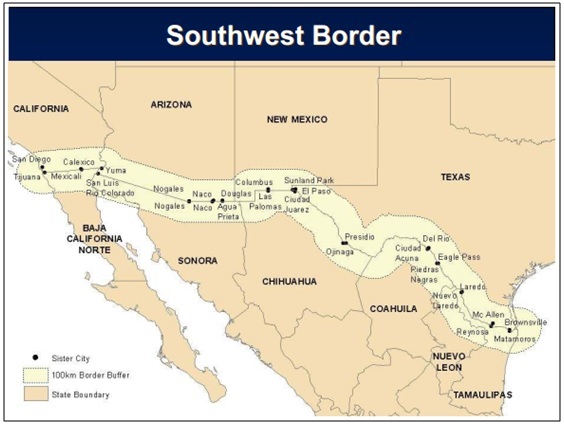 Notice Sister Cities Identified
Notice Sister Cities Identified
The La Paz treaty is documented in the U.S. State Department Treaties in Force as of January 1, 2009 on page 187 (Adobe). An extract of that report can be viewed HERE. The FULL REPORT can also be viewed.
Signed at La Paz August 14, 1983.
Entered into force February 16, 1984.
35 UST 2916; TIAS 10827; 1352 UNTS 67.
1990 Enterprise of the Americas
The Enterprise of the Americas Initiative – George Bush announcing the initiative for a “hemispherewide free trade zone“, June 27, 1990. Special recognition for the attendees: Members of our Cabinet — Nick Brady and Secretary Baker, Carla Hills, Secretary Mosbacher — delighted you’re here. Chairman of the Council of Economic Advisers, Mike Boskin, is here. Bill Webster, welcome. And of course, we’re delighted to see Alan Greenspan, Chairman of the Federal Reserve Board, here and then an old friend, Barber Conable, of the World Bank, and Richard Erb, from the IMF. And Ricky Iglesias, an old friend of the Bushes, and we welcome him, of the IDB, and so many leading lights in the business and financial communities.
George Herbert Traitor Bush:
• Throughout the region, nations are turning away from the statist economic policies that stifle growth and are now looking to the power of the free market to help this hemisphere realize its untapped potential for progress.
• . . . we must build on the trend we see toward free markets and make our ultimate aim a free trade system that links all of the Americas: North, Central, and South. And we look forward to the day when not only are the Americas the first fully free, democratic hemisphere but when all are equal partners in a free trade zone stretching from the port of Anchorage to the Tierra del Fuego.
The Enterprise was no doubt the kick-off of negotiations for NAFTA.
North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) – negotiations began by George Bush, signed by George Bush, but the Congress wasn’t ready to vote on it until 1993 – effective 1994.
December 8, 1993 President William J. Clinton signed the North American Free Trade Agreement Implementation Act NAFTA Worker Security Act. It became Public Law 103-182.
The legislation was H.R. 3450, passed by House on November 17, 1993 and by the Senate on November 20, 1993
December 8, 1994 President William J. Clinton signed the Uruguay Round Agreements Act Retirement Protection Act of 1994. It became Public Law 103-465.
The legislation was H.R. 5110, passed by the House on November 29, 1994 and by the Senate on December 1, 1994.
 George Bush announcing Enterprise for the Americas Initiative (C-span)
George Bush announcing Enterprise for the Americas Initiative (C-span)
 George H.W. Bush, Speech at the UN,
George H.W. Bush, Speech at the UN,
October 1, 1990, text of the speech
The Enterprise for the Americas Initiative, Description and Update, October 1992 *** Note reference to the environment
Summit of the Americas
Page 17, Sense of the Senate on Uruguay Round Implementation
Page 20, The Summit of the Americas
THE SUMMIT OF THE AMERICAS
Mr. President., this December, an important event will take place in Miami, FL, which should be of interest to all senators. On December 9 and 10, President Clinton will host the first meeting of democratically elected leaders in the Western Hemisphere. It is the first summit of its kind in over a generation, and it is intended to follow up on the signing of the NAFTA Treaty with Mexico which created the world’s largest free trade zone.
NOTE: Clinton Administration was loaded with Carter Administration re-treads; Warren Christopher for one.
OAS – History and Process for the Summit of the Americas. Note this paragraph concerning a common market agreed to in 1967.
“The final Summit of this period met in Punta del Este in 1967. The declaration, subscribed to by the presidents, included the creation of a Latin American Common Market by 1980 . . . Declaration of the Presidents of America, Punta del Este, Uruguay, April 14, 1967
Free Trade Area of the Americas by 2005
 Source: FTAA – Blueprint for Prosperity: Building on NAFTA’s Success
Source: FTAA – Blueprint for Prosperity: Building on NAFTA’s Success
FTAA and September 11, 2001

Samuel “Sandy Burglar” Berger: Nexus 9/11 and NAU
“As time went on, the seats formerly allocated to the defense and intelligence chiefs were occupied by representatives from such agencies as Commerce, EPA, and the agency most directly focused on the new security issues of international crime, the Department of Justice.” [pg 82 Summitry in the Americas: A Progress Report, Richard Feinberg]

Organization of American States
Free Trade Area of the Americas (FTAA)
FTAA – Blueprint for Prosperity: Building on NAFTA’s Success – Council of the Americas (Founder – David Rockefeller)